With the temporary shortage of some items at the grocery store in the first two years of the COVID pandemic, and now the rise in inflation, we see that we cannot take groceries for granted.
With every trip to the supermarket, we see our grocery list grow. Prices at the grocery store have risen more than 13 percent in the past year, according to the Consumer Price Index. This is the largest annual increase since 1979.
Our defense against COVID-19 has been bolstered by revolutionary vaccines that have been developed and delivered to millions, but we are not immune to the forces shaping our food supply: post-pandemic demand, bad weather in major agricultural areas crops, productivity and transportation. costs, and business disruption due to the war in Ukraine.
Food security is about affordability and availability, and the impact of the climate crisis is taking its toll on the latter. At the end of June, nearly half of the U.S. winter wheat crop (the type used for making bread) was in drought-prone areas, according to the USDA’s Drought Monitor. Half of the country’s livestock production is in dry areas, as well as 42% of durum wheat (a type of pasta), 56% of barley, 42% of dairy cattle, 41% of alfalfa and 35% of grass used. animal feed.
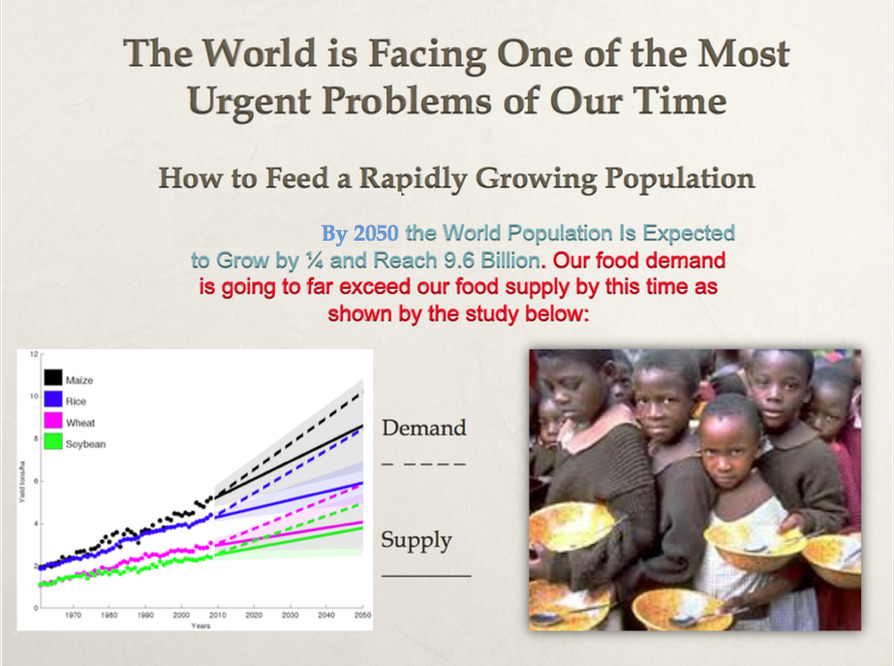
Things are worse than our borders. According to the United Nations report “The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World,” Hunger is on the rise in the world. More than 3 billion people will not be able to eat enough food in 2020 and about 828 million will be affected by hunger in 2021. Now, there is a humanitarian crisis in East Africa and parts of the Middle East as severe drought it destroyed the crops. animals. Unicef says one child per minute is being pushed into life-threatening malnutrition in 15 countries.
Meanwhile, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations says that global crop production must increase by 28 percent over the next 10 years to achieve food security – more than the increase in crop yields. that has been achieved in the past ten years. This will take a lot of soil and water. It would also require a lot of innovation to increase productivity without asking more from our planet.
The good news is that modern science offers hope and solutions that can be used to help agriculture feed our great planet. Scientists are developing drought-tolerant crops, heat-tolerant cattle, more nutritious foods, and foods that have longer lifespans.
Innovative companies like Bayer CropScience are developing corn and rice varieties that are more drought and heat tolerant, reducing the amount of water needed to grow them. Other companies including Corteva Agriscience and BASF are developing the next generation of pest-resistant soybeans—and increasing infestations is a growing concern as our climate warms.
A Minnesota company, Acceligen, has developed heat-resistant cattle, using genetic modification to create short coats, or “slicks,” that help the animals stay cool.
J.R. Company Simplot Co. uses biotechnology to grow potatoes and other non-perishable crops, reducing food waste and facilitating the delivery of fresh food to stores and consumers in remote locations.
Interesting agricultural discoveries happen every day. But these findings will only be true if we have a solid, science-based, well-established system. Unfortunately, the US government has failed to develop policies on biotechnology and genetic modification.
FDA’s recent efforts to develop a regulatory framework for animal biologics will ensure the health and safety of animals, consumers, and the environment while increasing value. However, dealing with the FDA on further development is difficult because the guidance document appears to be stuck at the Office of Management and Budget. In addition, the FDA has not yet issued its guidance on new plant varieties produced using genetic modification tools, while the review of new biotech plant varieties has been very limited in recent years. Formulation of food products and additives that reduce animal methane emissions take three to five years to be reviewed by the FDA.
While the USDA has updated its regulations for biotech plants, the agency’s development plan for exemptions from regulation is stricter for plants that can be produced using conventional breeding. Further updates are needed to ensure that biotechnologies also have a clear, efficient path to market.
Finally, the EPA has yet to issue its final regulations that address plant-based pesticides developed using new technologies—products that enhance plant growth and increase pest resistance and reduce the need for pesticide application.
This regulatory uncertainty is not limited to the United States. Mexico is a major market for U.S. farmers and ranchers, but the lack of scientific knowledge to manage new agricultural technologies is harming the continued deployment of agricultural technologies that are critical to continuing to feed the world and combat climate change. This uncertainty is compounded by a presidential order calling for a ban on the importation of genetically modified corn by 2024, despite confirming the safety and benefits of GM corn. If the law is implemented, the price of corn tortillas in Mexico will rise by 30% in the first year of the ban, according to a report by CropLife International and World Perspectives Inc., which is hurting Mexicans. Such a ban could prevent the kind of new farming methods we need to meet our food needs, today and tomorrow.
Agriculture and science are moving rapidly to meet food demand and adapt to climate change. Science is on our side, but time is not. We need effective, efficient government regulations, both in the United States and abroad, to strengthen food safety through innovation.
Michelle McMurry-Heath, Ph.D., is a physician-scientist and president and CEO of the Biotechnology Innovation Group.
For more news and ideas, visit www.Agri-Pulse.com.
What is the impact of genetically modified foods on individuals?
The results of most studies with GM foods show that they can cause some chronic toxic effects such as liver, pancreatic, renal, or reproduction and can change the hematological, biochemical, and immunologic parameters. On the same subject : What to do with all those missing this fourth of July.
What are the effects of genetically modified food? In addition, some additional general concerns include environmental pollution, unintentional gene transfer to wild plants, the possibility of creating new viruses and toxins, limiting access to seeds due to plant patents -GM food plants, threats to genetic diversity, religion, culture and ethical concerns. , and fear…
What is the impact of genetically modified?
Some of the benefits of genetic engineering in agriculture include increased crop yields, reduced food or drug costs, reduced need for pesticides, improved nutrition and food quality, resistance to pests and diseases, improved food quality, etc. health benefits for the growing world population. .
What is the impact of genetically modified foods on individuals on the environment?
Loss of Biodiversity: The use of some GM crops can have negative effects on non-target organisms and the environment. Read also : Food expiration dates are not based on science. Here’s What You Can Do. For example, the expansion of GM herbicide-resistant corn and soybeans, which are associated with herbicides, have destroyed much of the butterfly’s habitat in North America.
How has genetically modified food impact society?
Also, GM crops help to reduce the impact on the environment by using plant protection products, using more land to produce more food and preserving biodiversity, which it allowed different types of plants and animals to exist in nature. On the same subject : Can canning cause botulism?.
How is biotechnology related to food?
Biotechnology can be used to improve the processing of traditional food based on the principles such as the methods used in the production of Gari flour, frozen food and waste and starch obtained from cassava. Biotechnology can also help eliminate toxic substances, either through genetic engineering or through food processing.
How has biotechnology changed the food industry? In this modern age, the demand for food in the world has increased with the need to improve crops. Biotechnology provides the technology needed to produce high yields, plants with natural resistance to disease and pests, and potentially more nutritious and tasty foods.
Why is biotechnology in food important?
Food technology can benefit the consumer in two ways: by helping to grow food locally and by providing new, nutritious foods. As of July 2008, over a variety of food technology products are on the market and many are in development.
What is food science examples?
Food scientists help determine this ‘lifestyle’. Example: grated cheese. You need to know which microorganisms grow on cheese. Whether the color or taste changes during storage, etc.
What is food science used for? Food Science allows us to make better use of our food resources and reduce waste. Most of the food is of natural origin. How they harvest, process, distribute, store and prepare is a complex problem. A thorough knowledge of all the important aspects of the problem requires extensive training.
What are the 4 main topics of food science?
Food safety and microbiology. Food engineering. Food processing technology. Product development.
What are the 3 areas of food science?
His program consists of three axes, because it is recognized that cooking has three aspects, which are social, technical and technical.